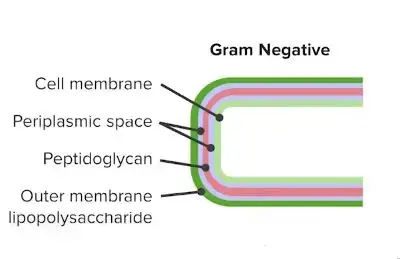
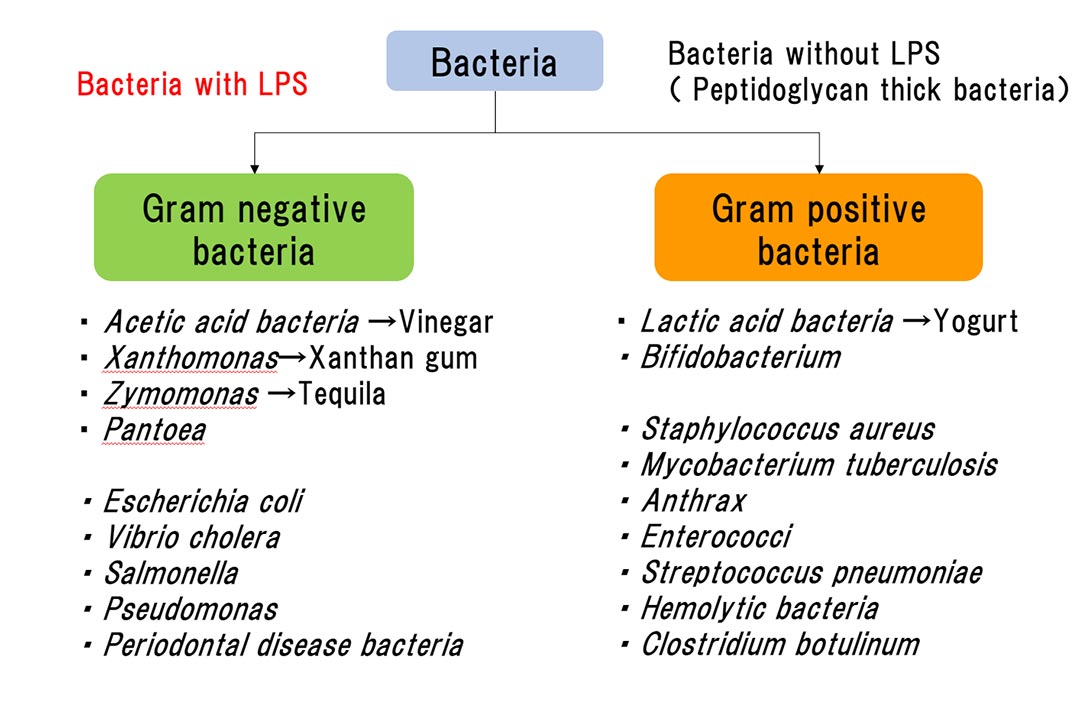
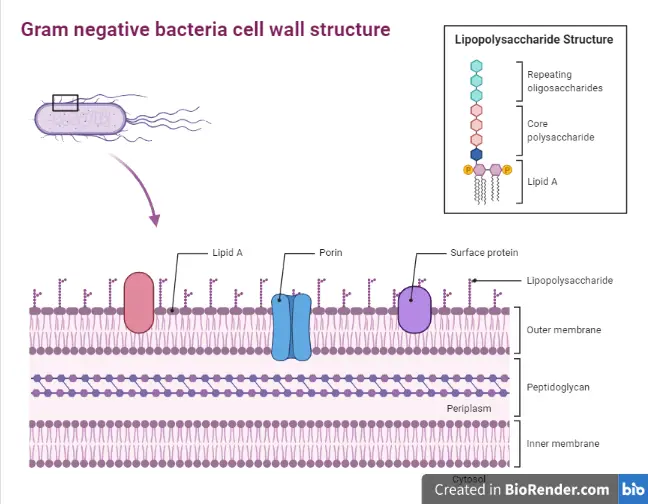
Accumulation of the cells in the growth zone after LPS injection. Some... | Download Scientific Diagram

Inhibition of the LPS-induced production of tumornecrosis-factor in... | Download Scientific Diagram
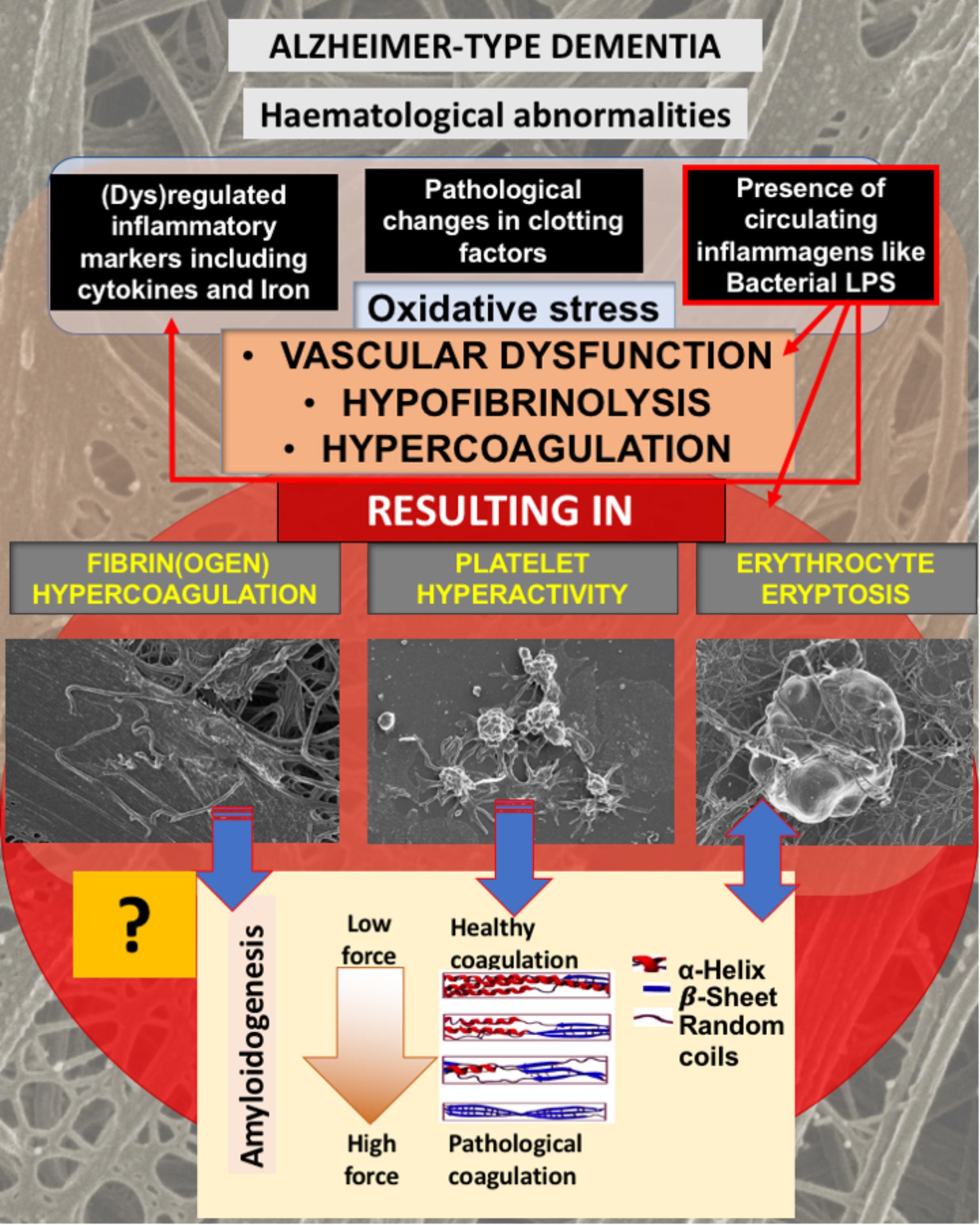
Frontiers | The Potential of LPS-Binding Protein to Reverse Amyloid Formation in Plasma Fibrin of Individuals With Alzheimer-Type Dementia
Pseudomonas aeruginosa LPS or Flagellin Are Sufficient to Activate TLR-Dependent Signaling in Murine Alveolar Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells | PLOS ONE

Variation in blood microbial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to immune reconstitution in response to suppressive antiretroviral therapy in HIV - eBioMedicine

Variation in blood microbial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to immune reconstitution in response to suppressive antiretroviral therapy in HIV - eBioMedicine
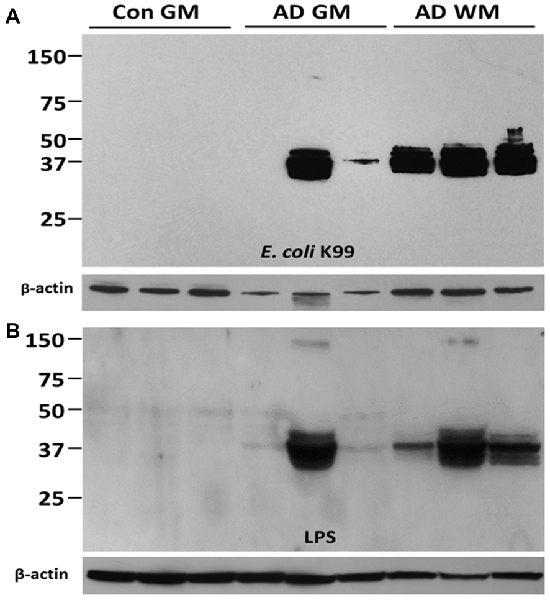
Frontiers | Lipopolysaccharide Associates with Amyloid Plaques, Neurons and Oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer's Disease Brain: A Review

Soluble β-(1,3)-glucans enhance LPS-induced response in the monocyte activation test, but inhibit LPS-mediated febrile response in rabbits: Implications for pyrogenicity tests - ScienceDirect

Hb subunits possess high affinity for bacterial LPS. S. minnesota LPS... | Download Scientific Diagram

Soluble β-(1,3)-glucans enhance LPS-induced response in the monocyte activation test, but inhibit LPS-mediated febrile response in rabbits: Implications for pyrogenicity tests - ScienceDirect

Variation in blood microbial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) contributes to immune reconstitution in response to suppressive antiretroviral therapy in HIV - eBioMedicine

Soluble β-(1,3)-glucans enhance LPS-induced response in the monocyte activation test, but inhibit LPS-mediated febrile response in rabbits: Implications for pyrogenicity tests - ScienceDirect