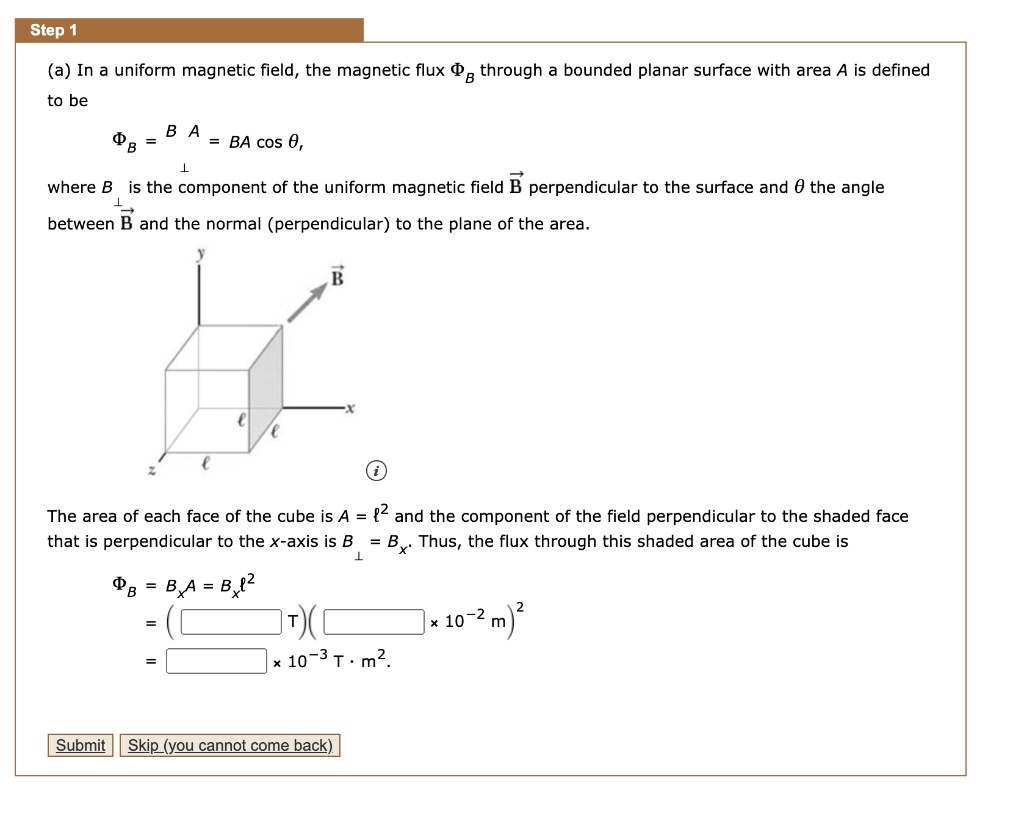
SOLVED: Step 1 (a) In a uniform magnetic field, the magnetic flux @B through a bounded planar surface with area A is defined to be B A BA cos 0, where B

electromagnetism - Why are there sine and cosine in the magnetic dipole moment (in the torque formula) of a rotating conductor loop? - Physics Stack Exchange

Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic Fields Produced by Currents In 1820, H.C. Oersted discovered that a current in a wire caused a deflection in. - ppt download
![The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by: vec(B)=B (0)hat(i)-[cos(kz- omegat)]+B(1)hat(j)cos(kz+omegat) where B(0)=3xx10^(-5)T and B(1)=2xx10^(-6)T. The rms value of the force experienced by a stationary charge Q=10^(-4)C at z=0 is The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by: vec(B)=B (0)hat(i)-[cos(kz- omegat)]+B(1)hat(j)cos(kz+omegat) where B(0)=3xx10^(-5)T and B(1)=2xx10^(-6)T. The rms value of the force experienced by a stationary charge Q=10^(-4)C at z=0 is](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/web-thumb/203513004_web.png)
The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by: vec(B)=B (0)hat(i)-[cos(kz- omegat)]+B(1)hat(j)cos(kz+omegat) where B(0)=3xx10^(-5)T and B(1)=2xx10^(-6)T. The rms value of the force experienced by a stationary charge Q=10^(-4)C at z=0 is

Evolution of an initial magnetic perturbation $\delta b=-0.5\cos (2\pi... | Download Scientific Diagram

shows the line-of-sight magnetic flux density calculated as B cos mag f... | Download Scientific Diagram
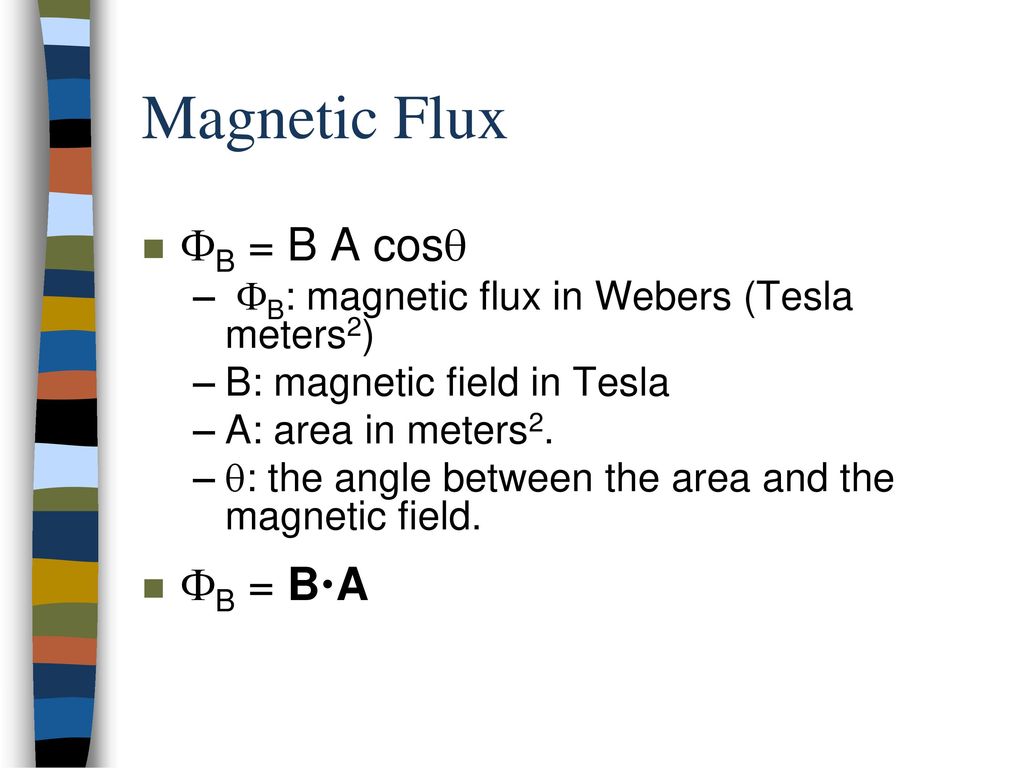
Faraday's Law Magnetic Flux cos BA Φ = : units Tesla m Weber Wb ⋅ = Faraday's Law (EMF Magnitude) Lenz's Law (EMF Direc

The electric field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by vec y = E0 vec i cos(kz)(ω t) The corresponding magnetic field vec B is then given by:

Magnetic field H = 2 π ( H 0 e y + H 1 (sin θ e x +cos θ e y )) changes... | Download Scientific Diagram

Normalized magnetic field components for the force free case in the... | Download Scientific Diagram

electromagnetism - Why are there sine and cosine in the magnetic dipole moment (in the torque formula) of a rotating conductor loop? - Physics Stack Exchange
![The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by: vec B = B0vec i [ cos ( kz - ωt ) ] + B1vec j [ cos ( kz + The magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by: vec B = B0vec i [ cos ( kz - ωt ) ] + B1vec j [ cos ( kz +](https://dwes9vv9u0550.cloudfront.net/images/9490195/d66b085b-b9ec-496d-97b4-742a1cdb7594.jpg)